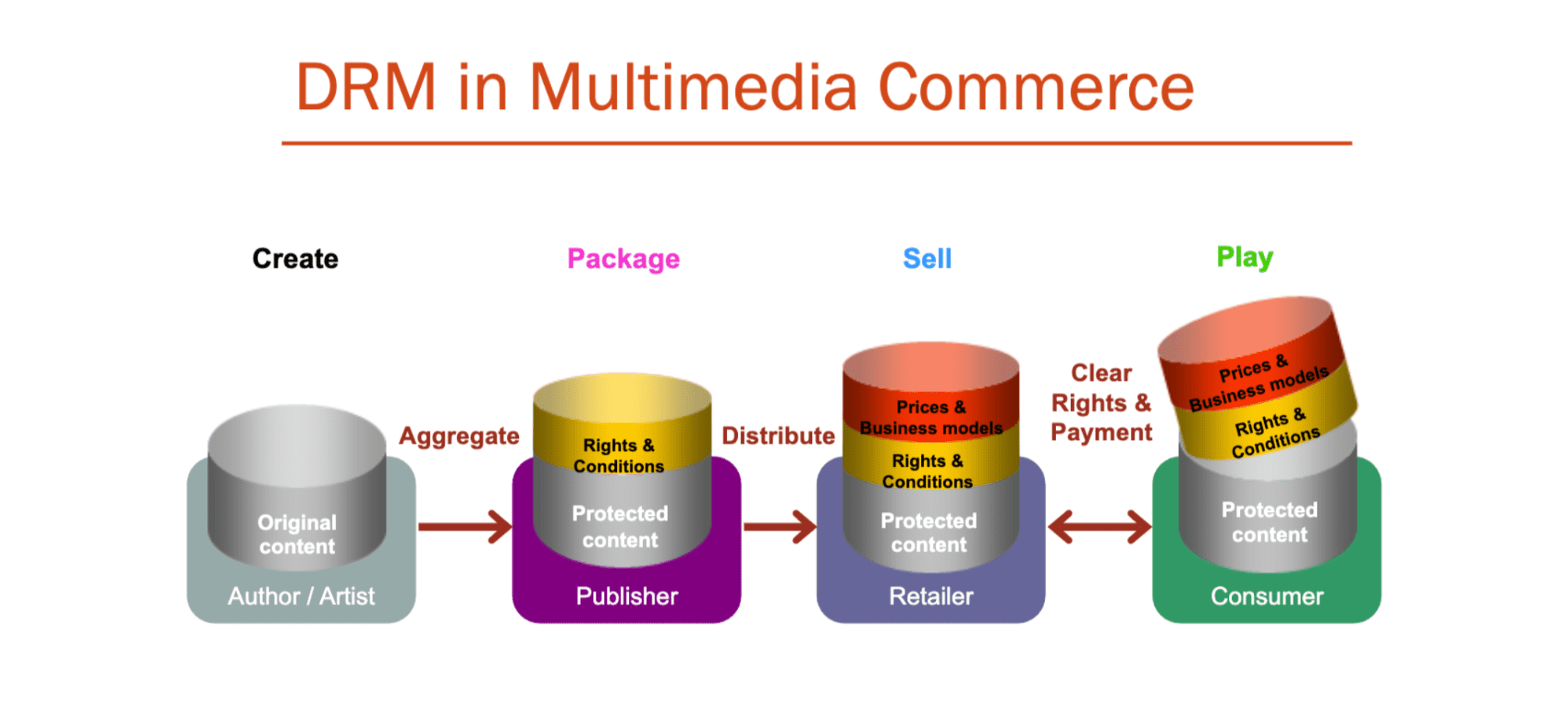
If you’ve never heard of Digital Rights Management (DRM) before then you’d be forgiven for thinking it was something that only publishing businesses needed to worry about. However, that’s not necessarily the case. Digital Rights Management can affect everybody, especially content creators. The more you know about it, the more you can be prepared as we venture further into the digital world of the future.
But what does DRM mean exactly?
What is DRM?
What does DRM stand for?
DRM stands for Digital Rights Management. It’s a term used to describe technologies and practices that are utilized to protect digital assets, as well as digital content, such as movies, music, and ebooks.
A DRM system is designed and employed to prevent unauthorized use or distribution of digital content. By controlling access to the content and limiting the ways in which it can be used, Digital Rights Management technologies are actively opposing digital age piracy.
DRM technologies usually use encryption techniques, among other security measures, to control access to digital content and restrict specific actions, such as copying or sharing. A DRM system may also implement software licenses to regulate the use of the content.
What is DRM-protected content?
When something is DRM-protected – meaning it has been encrypted by DRM technologies – then it can only be accessed and used in particular ways that are determined by the copyright owner. If unauthorized users access the digital content, then it would be classified as copyright infringement.
For example, DRM-protected content will likely have restrictions on a number of different aspects of the content’s use: the number of devices it can be used on, the number of times it can be accessed by the user, or the duration of its accessibility. These limitations are designed to prevent unauthorized access or distribution of digital content.
How does DRM work?
Digital Rights Management works by encrypting digital media, thus requiring users to obtain a license before they can access the content. The license will reveal the granular details of the terms and conditions under which the digital content can be used. It will often include restrictions (like the ones outlined above) and limit access to those who do not comply.
To access DRM-protected content, users generally have to work with special software programs, or sometimes specific devices, that have been built with Digital Rights Management in mind. These DRM software programs or devices will check and verify the user’s license to make sure that they are authorized to access the DRM-restricted content. They then decrypt the content so that the user can access it.
The type of DRM technologies used will depend on the content. Different types of digital content are protected in different ways. Movies and music, for example, may use different DRM technologies than ebooks or some kind of computer software.
Common DRM Technology
There are several well-known DRM technologies that you may have heard of:
- Amazon’s Kindle DRM system. This DRM technology is utilized by Amazon to protect ebooks bought on the Amazon Kindle Store from online piracy. Other ebook retailers and some libraries also use the same DRM technology.
- Apple’s FairPlay DRM software. When you make a purchase on the iTunes Store, this DRM software automatically protects your music and other digital content. The same Digital Rights Management system is used to protect other digital assets purchased via the App Store.
- Adobe’s Digital Editions DRM. Somewhat of a rival to Amazon’s Kindle DRM system, Adobe’s Digital Editions is designed to protect ebooks and other digital publications. Bookstores, libraries and other ebook vendors use this for their technological protection measures.
- Google’s Widevine DRM. Tons of streaming services use Google’s DRM service to protect their digital content. Android smartphones also utilize Google’s Widevine DRM technology to protect purchases made on the Google Play Store.
- Microsoft’s PlayReady DRM software. Devices that run on Windows are protected by Microsoft’s PlayReady DRM technology. It’s also used to protect digital assets and content purchased via Xbox.
As you can see, with 5 of the biggest names in technology using DRM software to protect their digital files, it’s obvious that Digital Rights Management and digital watermarking is here to stay. What’s not immediately obvious is where modern technology will take DRM.
For example, these big tech companies are notorious for being a hazard to data security; a big portion of their income comes from how they monetize your data. Now they are centrally governing your digital assets and telling you what you can do with them, where you can access them, and for how long.
Imagine buying a book and having the publishing company follow you around, telling you where and when you can read it, and for how long before they make you close it. It’s one thing to protect a creator’s rights; it’s another to meddle with a user’s purchase.
While Digital Rights Management is obviously important in today’s digital world, it’s also vital that the flaws in DRM technology get solved before it’s too late. With modern technology, DRM techniques are becoming more advanced, but they don’t have to become more restrictive.
Before we delve deeper into the downsides of DRM, let’s take a look at the benefits it provides.
What are the benefits of using Digital Rights Management?
The benefits may seem clear, but it’s still worth spelling them out.
- DRM protects intellectual property from online piracy. DRM can help digital content creators and distributors protect their intellectual property by making it difficult for unauthorized users to access and/or distribute it. This benefit of DRM technology helps creators get fair compensation for their work.
- Digital Rights Management encourages creativity. By providing a method to only allow authorized users access to digital content, DRM helps to create an environment in which content creators feel more confident and secure in releasing more content. However, as seen later, it can also have the opposite effect.
- DRM boosts security. Using encryption techniques, DRM protects digital content and makes a secure file that is only accessible to paying users.
While DRM was intended to be a good thing, things don’t always work out the way they were intended. Whether you’re dealing with audio files or an ebook, there are downsides to Digital Rights Management.
Is DRM bad?
Digital Rights Management is often controversial because it can limit the ways in which consumers can use the content they have purchased. This can be a bit of a pain if you bought an ebook, but want to read it from multiple devices (kindle, smartphone, etc.). Users often find it difficult to access content and this can put people off purchasing digital content that utilizes DRM, but more importantly, it can prevent sellers from using it, despite the piracy risks, in order to keep their customers happy.
There have also been critics who argued that DRM can be used to unfairly restrict consumer rights and stifle innovation. These critics suggest DRM solves nothing and only inhibits content creators and consumers alike.
Criticisms of Digital Rights Management
Here are some of the common criticisms of Digital Rights Management:
- DRM limits consumer rights. Digital Rights Management prevents users from copying or sharing their digital content with friends. This, in turn, limits the way in which users can interact with content that they purchased. In a sense, it’s like a big “but” attached to your purchase.
- DRM can be easily bypassed. It’s often seen as ineffective at protecting digital content because it can be overridden with relative ease. Most users can find a way around it if they really want to, which makes Digital Rights Management an annoying hurdle rather than an effective method to protect intellectual property.
- Digital Rights Management can be awkward to use. It is usually necessary to access digital content via a specific DRM software, adding extra steps to the process of accessing your fairly purchased digital files. This makes it incredibly difficult to access DRM content on multiple devices or platforms.
- DRM systems often collect data. DRM systems monitor how you interact with your digital files. Despite being built to prevent online piracy and attempt to adhere to copyright laws, DRM solutions see no problem with harvesting your data and sharing it among interested parties, including content creators and distributors.
- Digital Rights Management can suppress innovation. Contrary to the benefit of boosting creativity, Digital Rights Management can also suppress innovation. Because of the difficulty with making new products compatible with DRM-protected content, it has been argued that DRM is unnecessarily difficult for developers to use.
While Digital Rights Management sounds great on paper – protecting intellectual property from digital piracy – it clearly has its flaws.
So why are we talking about this here, at Elastos? What makes Digital Rights Management important today?
One word: blockchain.
How does blockchain technology affect Digital Rights Management?
Blockchain technology has the ability to impact Digital Rights Management in a number of different ways, each one strengthening the core concept behind DRM technologies.
- Immutable DRM. One of blockchain’s core tenets is that it’s immutable. It’s almost impossible to tamper with data that has been stored on the blockchain – that’s why this technology can be used to revolutionize so many industries.
If digital content was available as a non-fungible token (NFT), then it would be possible to track who owns it at all times. Not only this, but it would allow for the resale of digital content when the original purchaser is done using it. It creates digital scarcity, which automatically improves Digital Rights Management due to its inability to be reproduced in the same format. - Decentralized Digital Rights Management. Another key benefit of blockchain technology is its potential for decentralization. While some chains are more decentralized than others, DRM could thrive without influence or control of any one centralized authority.
- Transparent DRM. Another tenet of blockchain technology is its transparency. It doesn’t require you to trust corporations, instead you can trust code, and what’s more, you can see the blocks and monitor transactions for yourself. This allows everybody that wants to to track the ownership and usage of digital assets.
- Automatic Digital Rights Management. Utilizing smart contract technology, Digital Rights Management can be automated so that the terms of a DRM agreement are enforced through code. For instance, payment may be released to the content creator or distributor once a specific milestone has been reached.
Most of the problems with Digital Rights Management that exist today can be solved with the use of blockchain. NFTs have already started to gain traction as digital art; it’s only a matter of time before they become more popular for other digital content. There are tons of quality use cases available for NFTs as we transition from Web2 to Web3.
In addition to the four benefits outlined above, Elastos allows DRM technology to become even more powerful…
How does Elastos improve Digital Rights Management?
Elastos isn’t just a blockchain. It’s a smart contract platform that comes with a suite of features that developers can use to create decentralized applications for Web3, the metaverse, and whatever lies beyond.
- Peer-to-peer network. Elastos’ Carrier network is a fully decentralized peer-to-peer network that is designed to replace outdated IP addresses. Decentralized and fully encrypted, Carrier transmits information on behalf of dApps so that no middleman can interfere or surveil.
- Decentralized storage. Elastos’ decentralized storage system, Hive, empowers users to store their data in the same way that they would store their Bitcoin – safely, securely, and privately. Users remain in control of their data at all times.
- Decentralized identities. As we edge closer towards a dystopian technocracy, it’s important to decentralize areas which lack trust. Digital identities is one of them. With decentralized identities, you can keep one log-in for all Web3 websites, but maintain control over your data and information.
There can be no huge data leaks or breaches that reveal sensitive documents or information when the internet as we know it becomes decentralized. This will also be beneficial for Digital Rights Management, as each DID will be able to hold, sell, or trade its digital assets, including digital content.
So Elastos has the tech to decentralize DRM, as well as make it trustless and automatic. But is there any dApp to showcase such a thing?
Meet Elacity.
Elacity: bringing DRM to Web3
Elacity is a smartweb platform that facilitates the creation, management and distribution of digital assets using AI, digital rights management (DRM) and Web3 technology. It intends to utilize all of the Elastos tech stack to showcase what Elastos is capable of. It makes sense that they are the first ELA project to be thinking of combining NFTs with Digital Rights Management.
Working with Dr. Xin Wang, an expert in the field of Digital Rights Management, Elacity intends to combine a DRM and NFT system. This will introduce digital scarcity to digital assets and open up disruptive new business models which empower content creators to own their data and monetize it without third parties. Their first goal is to deliver a DRM-powered NFT video-sharing platform, comparable to a Web3 Netflix or YouTube.
The ultimate goal here is to bring Digital Rights Management (DRM) from the world of Web2 to the world of Web3. The project aims to add blockchain, a.k.a trust, to a pre-existing system (DRM) and showcase that you don’t need to rely on centralized parties to distribute royalties, protect assets, or ensure data rights are respected. By using blockchain to facilitate transactions in a trustless manner, we can effectively cut out the middleman and empower content creators to earn more, thus fuelling further innovation and creativity.
Not just for newcomers
Elacity’s bold vision of a merged NFT and DRM system isn’t just for new Web3 participants to enjoy. Traditional entities from Web2 may bring their contracts to Elacity by uploading them and simply clicking “Deploy“.
Behind the scenes, Elacity converts DRM contracts into EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) smart contracts and deploys them on the blockchain network. This allows existing creators to convert their real-world contracts into smart contracts and reap the rewards of Web3.
In addition, Elacity’s newly demonstrated interface enables users to choose who will receive royalties. In a movie, for example, there may be many different parties who are contracted to receive royalties. In the world of FIAT currency, these royalties may be paid out monthly or even quarterly; but when you implement DRM technology with NFTs, each transaction will automatically and instantly send the exact percentage of royalties directly to your wallet.
You can even choose how many wallets will receive royalties, with a number of early examples including: creator, publisher, distributor, and investor. This transparent way of delivering royalties is akin to livestream payments, and is extremely enticing to content creators who regularly have to sacrifice a lot of their potential revenue to middlemen.
Are there any downsides to merging blockchain technology with Digital Rights Management?
Of course, there are a few hurdles that blockchain must still overcome.
- Limited adoption. While the technology is fantastic at decentralizing power and making transactions more trustworthy and transparent, there is still a lack of adoption that will definitely put off content creators who are hoping to reach a large audience. If specialized software is needed to merge the two, then this may make it even more difficult for users to access the digital content.
- Scalability. One of the common problems of blockchain technology is its ability to scale. Elastos, however, uses a sidechain architecture, which allows it to scale infinitely by simply creating a new parallel chain whenever needed. Other blockchains have different scalability solutions, such as sharding.
- Cost. It may be more expensive to run a blockchain than the current DRM mechanisms, but again, this depends and can vary from blockchain to blockchain. As Elastos can scale relatively easily, there should not be a high cost associated with creating a DRM/NFT system. Gas fees are miniscule.
- Complexity. Off-puting for newcomers, blockchain technology is still in its infancy and most people don’t understand what a crypto wallet is, let alone how to mint DRM-NFTs. To implement DRM technology requires advanced cryptographic techniques and a distributed ledger system that can be challenging for content creators and distributors to comprehend.
Luckily, a platform like Elacity makes this easy for creators as all the technical magic happens in the background. Even physical contracts are converted to smart contracts behind a delightful user interface. - Security risks. As with all technologies, especially emerging ones, there are security risks that may hinder adoption. For example, there are more and more crypto hacks every single year, with billions of dollars stolen in total. Not only that, but content creators and/or distributors will have more responsibility in keeping their keys safe. If they lose the keys to their wallet, they lose access to their royalties and NFTs permanently.
The Essentials Super-Wallet has a user-friendly interface that makes looking after your crypto simple. But even Essentials requires you to take responsibility for your keys. Keep them safe at all times.
Blockchain isn’t perfect. But it’s a damn sight better than what we currently have.
If Bitcoin is decentralized money and DeFi is decentralized banking, blockchain-based DRM will become decentralized content creation.
If you want to be a part of it, log in to Elacity and have a look for yourself. You can check out their Tweets here or join the Telegram and say hello.